Lucia Lee
Last update: 07/11/2024
From chatbots like ChatGPT to Youtube video suggestions, machine learning is present in everyday life more often than you may notice. This critical branch of artificial intelligence (AI) drives innovation across various industries, but what exactly is machine learning, how does it work, and how is it being used? You’ll find everything you need to know about machine learning in this post. Let’s dive right into it!
Machine learning is a technology that allows computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without needing explicit programming. By identifying patterns and relationships within large datasets, machine learning algorithms can make predictions and decisions based on historical data analysis.
While some people use the term “machine learning” and “artificial intelligence” interchangeably, they are not the same thing. In fact, machine learning is a branch of AI, which refers to machines performing tasks that require human intelligence. You can find more about AI and its branches here.
Machine learning systems excel at analyzing vast amounts of data to make decisions. But what’s really happening behind the scenes? Below is an overview of how machine learning works:
Step 1: Data collection
First, relevant data is collected. Data is at the heart of machine learning, and it can come from multiple sources, including databases, text files, images, or even web scraping. Data must be directly related to the problem you want to address.
Step 2: Data preprocessing
Data must be processed before being fed to machine learning models. In other words, raw data needs to be turned into training data. This step is essential for improving data quality and ensuring the model can interpret it correctly, leading to more accurate results.
Preprocessing data can involve cleaning the data (removing duplicates, handling missing values, and correcting errors), transforming the data (normalization or scaling for a standard format), and dividing the data into training and test sets.
Step 3: Choosing a model
After preparing the data, the next step is selecting a suitable model. Common machine learning models include decision trees, linear regression, and neural networks, with more complex tasks sometimes requiring deep learning models. Your choice depends on factors such as data size, problem complexity, and available computational resources, as these elements impact the model’s ability to provide accurate results.
Step 4: Training the model
The model chosen now needs to be trained using the training data. In this step, the model processes the data, adjusting its internal parameters to recognize patterns and improve prediction accuracy. The goal is to minimize the difference between the model’s predictions and the actual results in the training set. Care is taken to avoid overfitting - where the model performs well on training data but poorly on new data, and underfitting - where it struggles with both.
Step 5: Evaluating the model
After training, the model’s performance is evaluated using test data. The goal is to test if the model can generalize well to new, unseen data. Common evaluation metrics include accuracy for classification tasks, precision and recall for binary classifications, and mean squared error for regression. By using these metrics, you can gain insights into the model’s effectiveness and readiness for deployment.
Step 6: Optimization
After testing, it is essential to fine-tune the model to boost its performance. This can involve adjusting the learning algorithms or applying feature engineering - creating new input features from the data to improve predictive power. The goal is to enhance the model’s accuracy, efficiency, and ability to generalize effectively to new, unseen data.
Step 7: Deployment
Finally, the trained and optimized model is put to use in a real-world setting, where it processes new data to make predictions or decisions. This involves feeding fresh data into the model, allowing it to generate outputs and help you solve problems.

How does machine learning work?
Machine learning is powered by algorithms - sets of rules that help machines recognize patterns within datasets. There are three main types of machine learning algorithms, including:
Supervised machine learning
Supervised machine learning involves training models on labeled datasets. This means each data point is tagged with the correct answer, or “label.”, allowing the model to learn patterns and make accurate predictions.
For instance, if given images of fruits labeled by type, the model can learn to identify each type of fruits in new, unlabeled photos. Supervised learning is widely used today, especially for tasks like classification and prediction.
Unsupervised machine learning
Unsupervised machine learning works by analyzing unlabeled data to find hidden patterns or groupings without pre-existing tags or labels. Instead of being guided by known outcomes, the algorithm identifies relationships and trends on its own.
For example, it can examine online sales data to uncover distinct customer segments based on buying behaviors. This approach is valuable for discovering insights in large datasets where categories or patterns may not be immediately obvious.
Semi-supervised machine learning
Semi-supervised machine learning is designed for situations where you have plenty of data but only a small portion of it is labeled. Instead of spending significant time and money labeling everything, this approach combines the strengths of supervised and unsupervised learning.
The model is first trained on the limited labeled data to establish initial patterns and decision boundaries. Once it has this foundation, the partially trained model begins analyzing the remaining unlabeled data and assigns labels to samples it feels confident about - a process known as pseudo-labeling. These newly labeled samples are added to the training set, and the model is retrained to improve its accuracy.
Reinforcement machine learning
Reinforcement machine learning enables algorithms to learn through trial and error within a structured reward system. By receiving feedback after each action, the algorithm gradually identifies the best strategies to achieve its objectives. For example, you can tell chatGPT to summarize a book, giving it feedback until it gives you a summary of the length you want.

Types of machine learning algorithms
Machine learning opens up endless possibilities, transforming how businesses across various industries operate. Let’s take a closer look at how some major industries are benefiting from machine learning.
Education
Machine learning helps educators monitor student progress, personalize learning paths, and automate time-consuming administrative work. It also supports the early detection of students who may need extra assistance, making education more adaptive, inclusive, and efficient.
Ecommerce
Machine learning brings the online shopping experience to the next level through personalized recommendations, optimized search results, and dynamic pricing strategies. By analyzing customer behavior, machine learning algorithms can predict preferences and tailor marketing efforts, helping businesses boost customer satisfaction and conversion rates.
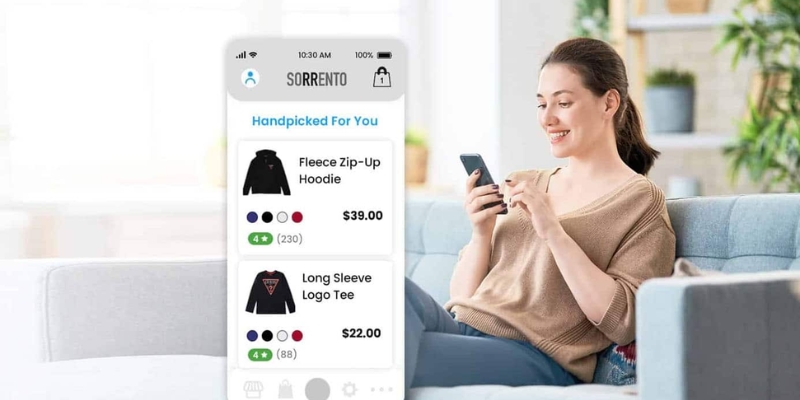
Use cases of machine learning in ecommerce
Transportation
In transportation, machine learning is used to optimize route planning, reduce fuel consumption, and improve traffic flow. It’s also the key driver of self-driving cars, helping them learn from road patterns and adapt to real-world driving scenarios for enhanced safety and efficiency.
Healthcare
Machine learning plays a crucial role in healthcare by aiding in early disease detection, diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans. With tools like image analysis and predictive analytics, it helps medical professionals make data-driven decisions, leading to more accurate and timely patient care.
Also read: Personalized Healthcare: Benefits, Solutions, and Trends
Finance
Machine learning supports fraud detection, risk assessment, and personalized financial advice in finance. It identifies suspicious activities and predicts credit risk by analyzing vast amounts of transaction data, allowing for more secure and efficient financial operations.
Manufacturing
Machine learning improves production efficiency by predicting equipment failures, optimizing maintenance schedules, and reducing downtime. By analyzing sensor data from machines, ML models can identify early signs of malfunction, improve quality control, and streamline workflows. This helps manufacturers cut costs, enhance product consistency, and maintain safer, more reliable operations.
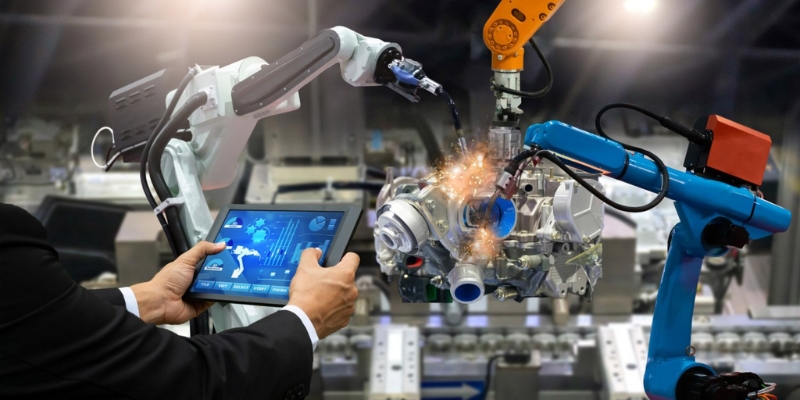

Use cases of machine learning in manufacturing
Security
In the security sector, machine learning strengthens threat detection, incident response, and overall risk management. ML systems continuously analyze patterns across networks, devices, or environments to identify unusual behavior before it escalates. From detecting unauthorized access attempts to flagging physical security risks, machine learning enables organizations to respond faster and prevent potential breaches.
Customer service
Machine learning elevates customer service by powering intelligent chatbots, predicting customer needs, and personalizing support interactions. By analyzing past conversations and user behavior, ML systems can resolve common issues instantly, recommend relevant solutions, and route complex cases to the right agents. This creates a smoother, faster support experience that boosts satisfaction and reduces operational costs.
Machine learning offers powerful advantages that help businesses operate smarter, move faster, and compete more effectively in data-driven environments. Let’s explore what machine learning brings to the table!
Automation of routine work
Machine learning streamlines repetitive, time-consuming tasks - from sorting emails and processing documents to categorizing large volumes of data. By offloading these activities to ML-driven systems, businesses boost productivity, reduce human error, and allow teams to focus on strategic, high-value work.
Cost reduction and operational efficiency
By automating workflows and optimizing processes, ML helps organizations save both time and money. Chatbots reduce the need for large support teams, predictive maintenance cuts repair costs, and logistic algorithms optimize routes to lower fuel consumption. These improvements drive substantial long-term savings.
Smarter, data-driven decisions
ML models excel at processing complex information in real time, providing leaders with clear, actionable insights. Whether forecasting demand, optimizing inventory, or diagnosing issues in healthcare data, machine learning supports faster, more confident decision-making and helps organizations respond proactively to change.

Smarter, data-driven decisions
Advanced pattern recognition
One of ML’s biggest strengths is its ability to uncover trends that humans often miss. Retailers use this capability to analyze customer behavior and deliver personalized recommendations, while financial institutions detect anomalies that signal fraud. These insights lead to better strategies and more tailored experiences.
Continuous learning and improvement
Unlike static rule-based systems, machine learning becomes more accurate as it processes additional data. This self-learning nature makes it ideal for dynamic scenarios such as fraud detection, predictive maintenance, or personalized marketing - areas where conditions shift constantly.
Scalability for large datasets
ML systems are built to handle vast, complex datasets effortlessly. From analyzing sensor data in autonomous vehicles to managing information generated by enterprise systems, machine learning delivers reliable, real-time performance even as data volumes scale.
Better customer experiences
Machine learning enhances every stage of the customer journey. Businesses use ML to personalize recommendations, analyze feedback, and tailor communications across channels. With faster responses and more relevant interactions, companies strengthen loyalty and improve satisfaction.
While machine learning offers tremendous value, it also comes with significant challenges that businesses must navigate for effective implementation:
Heavy dependence on high-quality data
Machine learning models are only as good as the data they learn from. Incomplete, inconsistent, or biased datasets can lead to inaccurate predictions and unfair outcomes - particularly in sensitive areas such as hiring, lending, or healthcare. Ensuring clean, representative, and unbiased data is often one of the most demanding and expensive parts of any ML project.
High computational and operational costs
Training ML models - especially deep learning systems - requires powerful hardware, robust infrastructure, and skilled professionals. These costs can be substantial, making advanced ML development difficult for smaller organizations. Scaling models to handle massive datasets or real-time processing further increases resource demands.
Model complexity and lack of transparency
Many ML systems operate as “black boxes,” making it difficult to understand how decisions are made. This lack of interpretability raises ethical and regulatory concerns in industries like finance, insurance, and healthcare, where transparency is critical. Improving explainability without compromising accuracy remains an ongoing challenge.
Risk of bias and unfair predictions
Even when data is clean, it can still reflect hidden societal or historical biases. When models learn from imbalanced or skewed data, they may reinforce these patterns - such as prioritizing certain demographics or misclassifying minority groups. Correcting for bias often requires additional techniques like data resampling, anomaly detection, and specialized evaluation metrics.
Overfitting and underfitting issues
Striking the right balance between model complexity and generalization is difficult. Models that overfit learn noise instead of meaningful patterns, while underfitted models fail to capture essential information. Both scenarios lead to poor performance in real-world applications.
Data privacy and security concerns
Machine learning systems often rely on sensitive or proprietary data, exposing organizations to privacy risks and potential cyberattacks. Malicious actors may attempt to tamper with training data (data poisoning) or extract private information through model outputs. Businesses must implement strong privacy protections, staff training, and security controls to safeguard data throughout the ML lifecycle.

Data privacy and security concerns
Potential job displacement
Automating repetitive tasks can improve productivity but may also replace certain roles - particularly jobs involving routine data processing or manual operations. While machine learning creates new opportunities, helping workers reskill and transition into higher-value roles remains a significant challenge for many industries.
Successfully adopting machine learning requires a structured approach. By following a well-defined implementation lifecycle, your business can move from identifying a problem to deploying and maintaining reliable ML solutions.
Start with a clear business goal
Begin by defining what you want to achieve and why ML is the right approach. Identify the business problem, the value a solution would bring, and the measurable outcomes you expect - such as reducing errors, improving forecasting accuracy, or automating a manual process. A goal-driven plan helps secure stakeholder support and ensures ML initiatives align with strategic priorities.
Translate the business problem into an ML problem
Once the objective is clear, reframe it in technical terms: What input data is available? What output should the model predict? Which performance metrics - accuracy, recall, precision, or error rate - best reflect success? Proper problem framing sets realistic expectations and guides your team toward the right model and data strategy.
Prepare and process your data
High-quality data is the foundation of any ML system. This step involves collecting relevant datasets, cleaning and normalizing them, handling missing values, and engineering features that help the model recognize patterns. Effective data preparation ensures your model learns from accurate, consistent, and meaningful information.
Develop and deploy the model
With clean data in place, your team can train, test, and fine-tune the model to achieve optimal performance. At this stage, establishing MLOps practices becomes essential. MLOps helps automate the ML pipeline - from data processing and model training to deployment - so updates and improvements can be rolled out consistently. CI/CD pipelines are often used to push models into staging and production environments with reliability and speed.
Continuously monitor and improve performance
Machine learning models degrade over time as new data patterns emerge. Monitoring ensures the model stays accurate, stable, and aligned with business needs. This involves tracking performance metrics, detecting anomalies, and gathering real-world user feedback. Regular retraining or updating keeps the system effective and relevant.
In conclusion, machine learning is no longer just a futuristic concept but a powerful tool driving significant improvements in efficiency, customer experiences, and decision-making for businesses across various industries. At Sky Solution, we offer tailored machine learning solutions designed to meet the unique needs of your business, helping you unlock the full potential of your data. Fill out this form here to explore how we can support your business with cutting-edge AI and machine learning technologies!