Lucia Lee
Last update: 14/10/2025
Facial recognition has transformed the way businesses operate and how customers engage with them, unlocking new opportunities in security, operational efficiency, and customer experience. From preventing fraud to streamlining access and delivering more personalized interactions, more and more businesses are adopting this game-changing technology to stay ahead of the competition. In this guide, we’ll explore how facial recognition works, its key applications, and where the technology is headed next.
Facial recognition is a vital computer vision task that uses a person’s unique facial features to confirm or verify who they are. This form of biometric identification technology analyzes key landmarks - such as the eyes, nose, and jawline - and transforms them into a digital template for identity verification.
Facial recognition vs. related terms
When learning about this technology, you may come across related terms like biometric authentication and facial recognition. It’s crucial to understand the differences among them:
Also read: Computer Vision Tasks: Everything You Need To Know
Facial recognition may seem complex, but how does it actually work behind the scenes? It combines a variety of technologies that follow a logical process. Here’s how facial recognition works its magic:
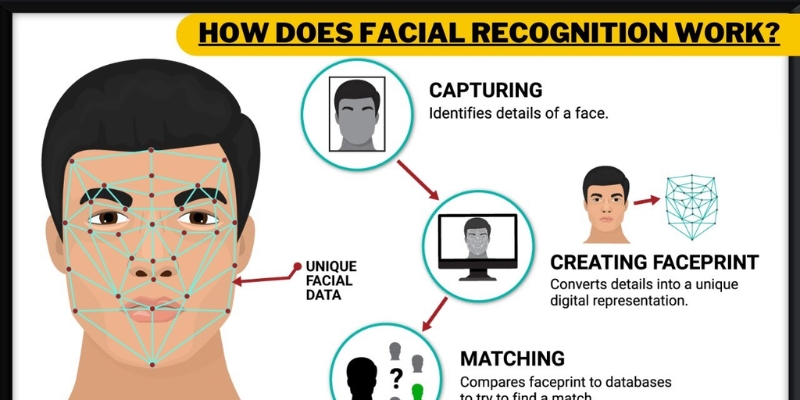
How facial recognition works
Step 1: Image capture
A camera (smartphone, kiosk, CCTV, etc.) takes a still photo or video frame of the person, which is the raw input for all subsequent image processing and matching.
Step 2: Face detection
The system scans the captured frame and locates any faces, separating the face region from background clutter and other objects. Advanced systems can find faces even in crowded scenes, partial profiles, or variable lighting.
Step 3: Feature extraction
Once a face is isolated, the software maps key landmarks (eye corners, nose tip, mouth, jawline) and normalizes the pose and scale. Those landmarks and pixel patterns are converted into a compact numerical representation - a vector or embedding - that captures the face’s unique geometry and appearance. This encoding step is driven by machine learning and deep learning models trained to produce stable, discriminative face embeddings.
Step 4: Template creation
The extracted embedding is turned into a secure template (often called a “faceprint”) that represents that individual. Templates can be stored locally on a device or in a protected database, and may be encrypted or converted into cryptographic keys to enhance privacy and tamper resistance.
Step 5: Comparison
When identity must be checked, the system captures a new image, repeats detection and feature extraction, then compares the new template against stored templates. Matching algorithms compute similarity scores between vectors to find candidate matches quickly and efficiently.
Step 6: Verification
The final step of facial recognition is to evaluate the similarity score against a threshold and apply contextual checks (time, location, device) before making a decision.The captured template is fed into an authentication system workflow that combines match confidence, anti-spoofing checks, and policy rules to accept, reject, or flag the attempt.
What once seemed like science fiction has now become part of everyday business operations. Let’s explore how businesses across industries are adopting facial recognition:
Employee attendance management
Facial recognition has transformed how companies handle attendance. Instead of relying on traditional time clocks or fingerprint scanners, businesses now use facial recognition systems that ensure both hygiene and accuracy due to their contactless nature. AI-powered platforms automatically record employee attendance and generate digital reports to monitor productivity. This not only saves administrative time but also enhances workforce efficiency - whether employees are working in the office or out in the field.
Access control
Facial recognition enhances access control in workplaces, factories, and residential buildings. It allows only authorized individuals to enter restricted zones such as offices, laboratories, or data centers - without the need for physical keys or cards. This not only tightens security but also provides a seamless, touch-free experience for employees and visitors alike.
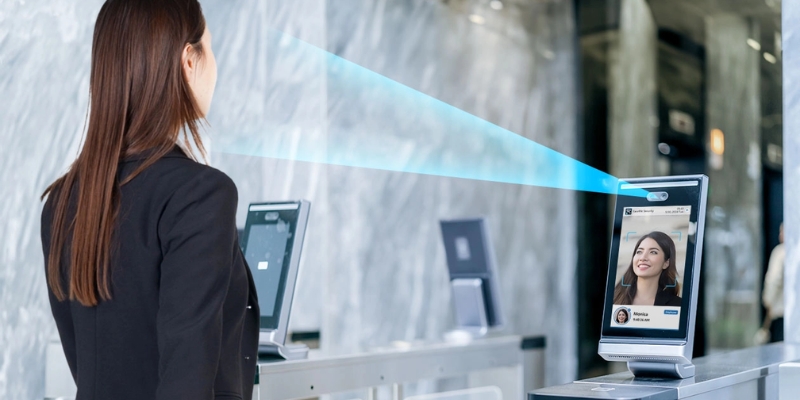

Access control
Smart retailing
Facial recognition has emerged as a game-changer for retailers, helping reduce shoplifting while taking customer experience to the next level. For example, it can detect known offenders to prevent retail crime. Cameras equipped with this technology can also recognize repeat customers and alert staff to offer personalized assistance or product suggestions.
Airports and border security
At airports worldwide, facial recognition systems speed up passenger check-in and boarding by verifying travelers’ identities in seconds. The technology minimizes waiting times and ensures a smooth yet highly secure travel experience. It also helps border control agencies detect unauthorized travelers or individuals on watchlists, reinforcing national security measures.
Law enforcement and crime prevention
In law enforcement, facial recognition plays a crucial role in identifying suspects and preventing crimes. Cameras equipped with this technology can match faces captured on video surveillance systems against criminal databases, providing instant alerts when a wanted person is detected. Officers can also use mobile devices to compare photos taken in the field with official records, helping to locate missing persons or verify identities in real time.
Also read: Facial Recognition AI Camera: Everything You Need To Know
Fintech and payment systems
In the financial sector, facial recognition enables secure and convenient payment processes. Say goodbye to easily hacked passwords as now customers can authorize transactions by simply scanning their faces, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. This biometric verification method adds another layer of protection to digital wallets, e-banking platforms, and fintech apps, making payments faster and safer for users.
Healthcare and hospital management
Hospitals are increasingly adopting facial recognition to improve patient safety and care. The technology helps identify patients accurately, streamline check-ins, and reduce medical errors caused by mistaken identity. In assisted living facilities, it can monitor patients’ movements and quickly alert staff if someone goes missing, ensuring safety and peace of mind.
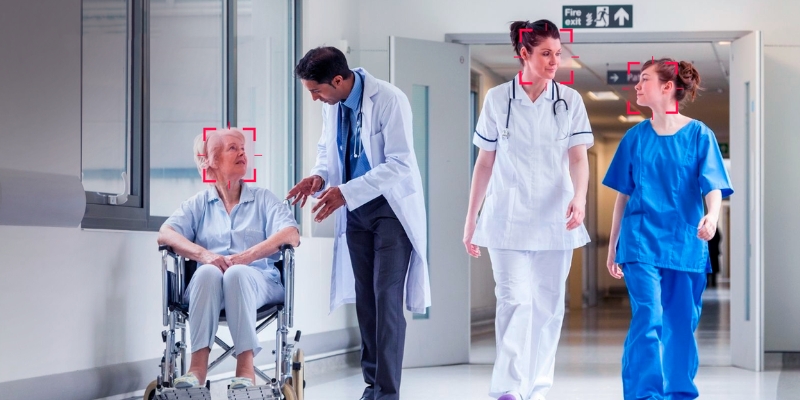

Healthcare and hospital management
Marketing and advertising
Facial recognition is becoming a valuable tool for marketers to understand audience reactions and tailor their campaigns accordingly. By analyzing facial expressions during product launches, events, or even in front of digital billboards, brands gain valuable insights into consumer engagement. This data-driven approach allows businesses to deliver personalized messages to their audiences.
Also read: Personalization in Ecommerce: Benefits, Examples, and More
Education monitoring
Schools are increasingly using facial recognition to automate attendance tracking and strengthen campus security. Students simply look into a camera to verify their identity, making recordkeeping seamless and efficient. Beyond convenience, the system also helps prevent unauthorized individuals from entering school grounds - protecting both students and staff while maintaining a safe, controlled learning environment.
Facial recognition is more than just a security upgrade - it’s a powerful business enabler that brings various benefits to organizations across industries, including:
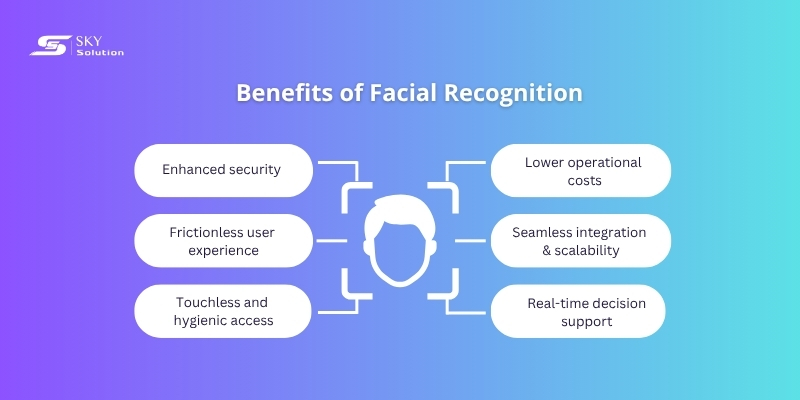
Benefits of using facial recognition for businesses
Enhanced security and fraud prevention
Every face is unique, making facial recognition one of the most secure authentication methods available today. When combined with liveness detection, it becomes nearly impossible for attackers to spoof or replicate. Businesses can use it to prevent unauthorized access, safeguard sensitive information, and strengthen their digital security posture without relying on passwords that can be stolen or shared.
Faster and frictionless user experience
Facial recognition eliminates the need for PINs, passwords, or physical badges. Users can log in, verify identities, or complete payments simply by looking at a camera. This not only speeds up processes but also reduces login friction, improving user satisfaction, onboarding, and conversion rates.
Touchless and hygienic access
In an age where contactless systems are becoming the norm, facial recognition offers a hygienic and effortless solution. Whether in healthcare facilities, corporate offices, or retail stores, employees and customers can gain access without touching shared devices, enhancing both safety and convenience.
Lower operational and support costs
Password resets and account recovery requests are major drains on time and resources. By enabling passwordless access, facial recognition reduces IT support tickets, streamlines identity verification, and cuts down administrative overhead, freeing teams to focus on higher-value tasks.
Seamless integration and scalability
Modern facial recognition solutions integrate easily with existing access control and enterprise management systems. This flexibility allows businesses to adopt biometric verification without costly infrastructure changes, ensuring a smooth transition and scalable deployment across departments or branches.
Real-time decision support
Facial recognition systems excel at pattern recognition and automated image analysis, identifying individuals faster and more accurately than manual checks. This gives organizations greater confidence in decision-making, fraud detection, and customer authentication.
While facial recognition offers immense potential, it also comes with complex challenges that businesses and governments must carefully address.
Privacy concerns & legal issues
One of the most pressing challenges of facial recognition lies in privacy concerns and data privacy. Because facial recognition systems collect and analyze biometric data, users often fear how their facial information is captured, stored, and shared. Mismanagement or unauthorized use could lead to intrusive surveillance and loss of personal anonymity. Governments worldwide are now debating strict regulations to ensure transparency and ethical use - especially as large-scale databases continue to expand. The growing public unease over privacy concerns & legal issues underscores the need for clear data protection frameworks.
Also read: CCTV Privacy Concerns: The What, Why, and How
Accuracy challenges
Despite advancements in AI & deep learning models for face recognition, the technology is not flawless. Variations in lighting, camera angles, facial expressions, or physical changes such as hairstyles and glasses can affect performance. Misidentifications can have serious consequences - ranging from false arrests in law enforcement to denied access in corporate environments - highlighting the ongoing accuracy challenges that still need to be overcome.
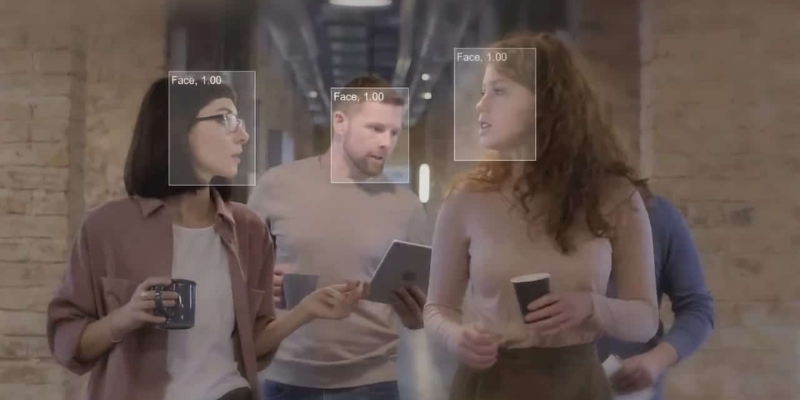

Accuracy challenges
Algorithmic bias and ethical risks
Like many artificial intelligence systems, facial recognition can reflect the biases present in its training data. If the algorithms are trained predominantly on limited demographic groups, they may misidentify or underperform for underrepresented populations. This bias not only reduces fairness but also raises broader ethical questions about equality, accountability, and discrimination in automated decision-making.
Security risks and data misuse
Although facial recognition strengthens security, it also introduces new vulnerabilities. Biometric data, once compromised, cannot simply be “reset” like a password. Cybercriminals could exploit stolen templates or use deepfakes to deceive weaker systems. The use of third-party providers also raises ownership issues - users often consent unknowingly to having their images stored and processed, creating additional data privacy and control challenges.
Public acceptance and trust
Facial recognition often divides public opinion. While many people welcome its convenience and safety benefits, others worry about constant monitoring and mass video surveillance. Gaining public trust requires transparency, responsible deployment, and strong governance. Companies that communicate clearly about data handling and consent are more likely to earn long-term acceptance.
As facial recognition continues to evolve, it’s shifting from a security-focused tool into a core enabler of seamless, personalized, and privacy-conscious digital experiences. Below are key trends shaping the next generation of this technology.
3D facial authentication
Unlike traditional 2D systems, 3D facial authentication maps facial contours in three dimensions, offering greater precision and resistance to spoofing. It can function reliably even in low-light environments or at unusual angles. This technology is already used in smartphones and is expected to expand into sensitive sectors like finance, border control, and healthcare.
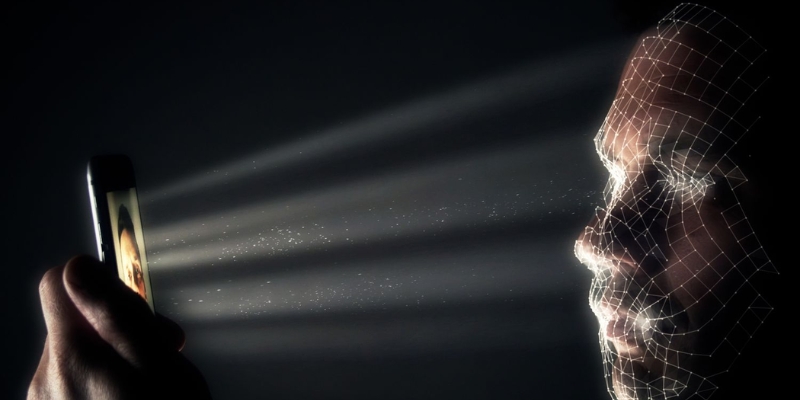

3D facial authentication
Contactless transactions
Facial recognition is redefining how people pay, check in, and access services - no physical contact required. From retail counters to airport gates, contactless facial authentication links a person’s face to secure payment or identity systems, reducing queues and enhancing hygiene. Industry leaders such as Mastercard and Alipay are actively testing these solutions.
Edge computing integration
The use of edge computing allows facial recognition to process data directly on devices instead of sending it to the cloud. This not only boosts speed and responsiveness but also enhances privacy by minimizing data exposure. As on-device AI becomes more capable, local facial analysis will become the norm for faster, safer verification.
Automatic ‘no-enrollment’ systems
Next-generation platforms are simplifying setup through auto-enrollment features. Instead of manually registering users, systems can securely generate biometric templates from existing data sources such as HR databases or access control systems - saving time while maintaining consent and control.
Smarter liveness detection
Future facial recognition won’t just identify faces - it will confirm that users are real and present. Advanced liveness detection will analyze micro-movements like blinking, gaze shifts, or facial reactions to prevent spoofing attempts. These improvements add another layer of trust for high-security use cases.
Ethical and legal guardrails
As adoption grows, concerns about privacy, bias, and consent are driving the need for stronger ethical and legal frameworks. Governments and organizations are working toward transparent policies, consent-based models, and user opt-outs to ensure responsible use and maintain public trust.
Blockchain-based data security
To address vulnerabilities in centralized databases, researchers are exploring blockchain for storing encrypted biometric data. Its decentralized and tamper-proof design could give individuals more control over their facial information and ensure data integrity across systems.
Augmented reality for verification
Augmented reality (AR) is making facial authentication more interactive and secure. By guiding users through real-time movements - like turning their head or smiling - AR adds a responsive layer of verification. Over time, this could merge biometric security with user experience design in everyday digital interactions.
Facial recognition is rapidly transforming the way businesses enhance security, streamline operations, and deliver personalized experiences. As this computer vision technology continues to evolve, its applications will only become more precise, efficient, and accessible.
At Sky Solution, we help businesses harness the power of AI-driven facial recognition and other computer vision solutions - designed to fit your unique needs and goals. Bring smarter, safer, and faster automation to your business with Sky Solution today. Contact us now for a free consultation!